Case study: Vercel documentation feedback system
How Vercel collects user feedbacks about its documentation pages with a step by step guide to replicate it in your own documentation with Feelback
In this article we’re going to analyze the Vercel documentation feedback system, how it works and how to add a similar system on your website.
How Vercel documentation collects feedback
At the end of each article, the Vercel documentation asks the user to evaluate the page. If you scroll down to the bottom, the page displays a question with four reaction emojis:
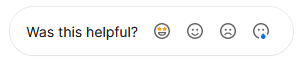
When the user click one reactions nothing is sent yet. Instead, a textarea appears where the user can type on optional message before sending the feedback.
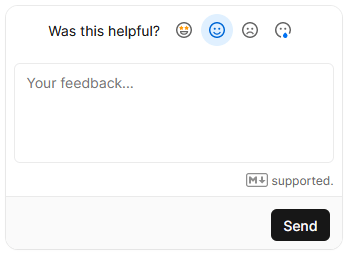
Let’s analyze in detail how the Vercel feedback collection works.
Where is asked?
Vercel documentation asks for feedback in all documentation pages. At the bottom of each page, the question Was this page useful? ends the article asking the user to evaluate the content.
Each documentation page provides valuable information to the user, so it’s useful to know what the user thinks about that information.
What is collected?
The Vercel documentation feedback is quite simple. It’s composed by two fields:
- a reaction (or tag)
- a text message
To make the user choice as a matter of feeling about the page, the UI presents the categories as a set of emoji reactions.
Vercel chose to have the message optional. This will further reduce the user psychological load and will result in an higher volume of feedback collected.
How is asked?
Vercel asks to evaluate the page by picking a reaction. To ease the process, a simple leading question reveals the optional message that can be sent.
The short question with a simple reaction choice is easily understood by the user, just with a glance. The common emojis buttons further help to communicate what is the expected interaction with familiar elements. In addition, the optional textarea reveal mechanism reduces the user friction caused by a larger quantity of information to parse and digest. The less the info, the more likely the user will understand and act upon.
How to add a Vercel-like feedback system in your website
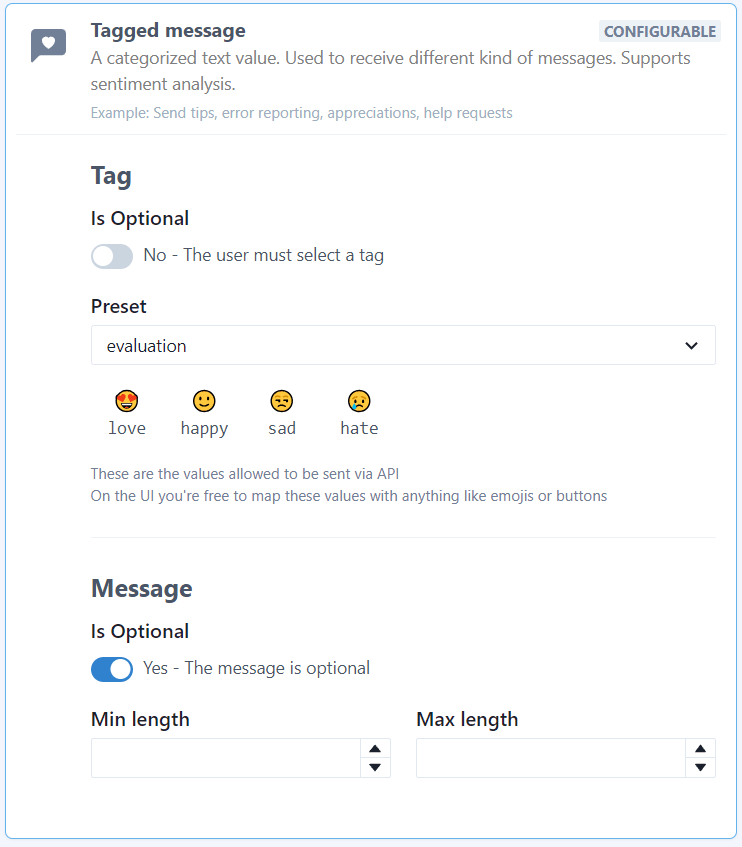
We’re going to use Feelback to easily add a Vercel-like feedback system on your website. In particular, we’ll use the Tagged Message feedback to collect categorized messages from your users.
Step 1: Project setup
If you don't have already a Feelback account, please signup and create one. It's free and doesn't require a credit card to use.
Access the Feelback panel, and create a project if you don't have any.
You can use your website name.
After that, create a ContentSet which will contain your content and feedbacks you will receive.
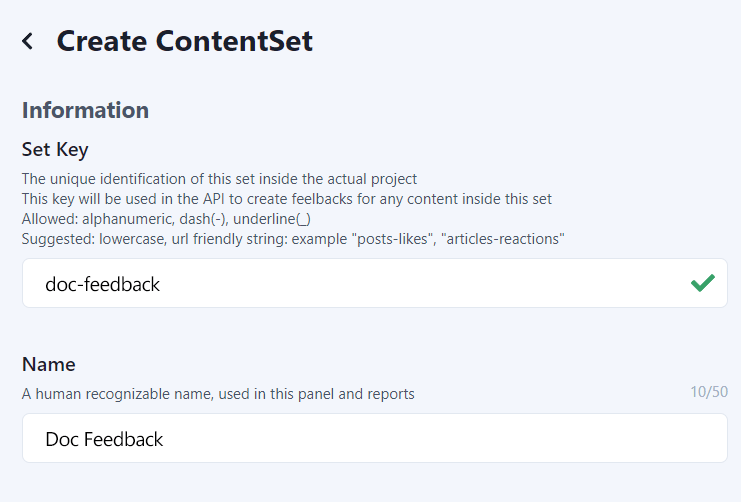
Pick the Tagged Message type to enable this content-set to receive categorized feedback message signals.
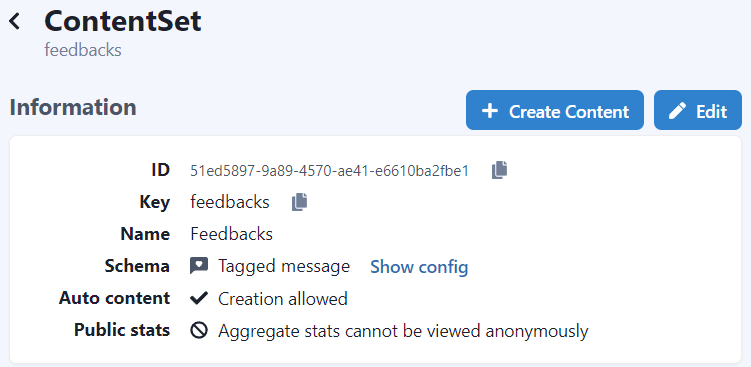
You will end up with a ContentSet like the following one:
Step 2: Install the Feelback plugin
For this guide we’re going to assume you have a React-based website. Therefore, the next steps will focus on how to integrate a Feelback React component.
If your website is not build with React, Feelback offers integrations with many different libraries, static generators and site builders, where the same steps outlined here will apply.
For React, Feelback provides the dedicated @feelback/react integration package. In your project directory, you can install it with your preferred package manager:
npm install @feelback/reactpnpm add @feelback/reactyarn add @feelback/reactStep 3: Add the FeelbackTaggedMessage component to the layout page
Now you are ready to collect feedback for your article pages. Let’s suppose you have a Article component for the documentation page.
Just import the FeelbackTaggedMessage component and add it at the end of the article content.
import "@feelback/react/styles/feelback.css";
import { FeelbackTaggedMessage, PRESET_EVALUATION } from "@feelback/react";
export function Article() {
return (
<article>
{/* article content here */}
<hr />
<FeelbackTaggedMessage contentSetId="$content-set-id-from-panel"
preset={PRESET_EVALUATION}
layout="reveal-message"
title="Was this page useful?"
placeholder="(optional) Type your feedback"
/>
</article>
);
}Step 4: Customize the style (Optional)
Builtin styles
You can use some builtin styles to personalize the appearance. You use the style prop of the component:
// one
<FeelbackTaggedMessage contentSetId="$content-set-id-from-panel"
preset={PRESET_EVALUATION}
layout="reveal-message"
style="bordered"
title="Was this page useful?"
placeholder="(optional) Type your feedback"
/>
// or multiple
<FeelbackTaggedMessage contentSetId="$content-set-id-from-panel"
preset={PRESET_EVALUATION}
layout="reveal-message"
style={["bordered", "width-sm"]}
title="Was this page useful?"
placeholder="(optional) Type your feedback"
/>Available styles:
| style | description |
|---|---|
| bordered | add a thin rounded border with some padding around the form |
| align-center | align the content to the center |
| width-sm | set the max-width to 320px |
| width-md | set the max-width to 440px |
Custom style
For total control, you can override the predefined style with additional CSS.
For example, you can add some selector to change the buttons background.
custom.css
.feelback-container .feelback-btn {
background-color: "cyan";
}Full documentation with advanced customization is available at the React integration guide.
Analyze aggregated feedback data
You can access the Feelback panel and checkout your content performance. A content item is the target object of the user feedback. In this scenario, a content item is the actual page the user is browsing.
In the dashboard, you can quickly see which page performs better.
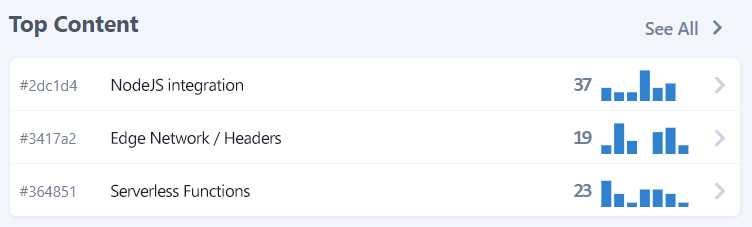
For each page you can analyze aggregated data, which include the feedback count received. You can go back and check historical data and change the aggregation period to week, month or year.
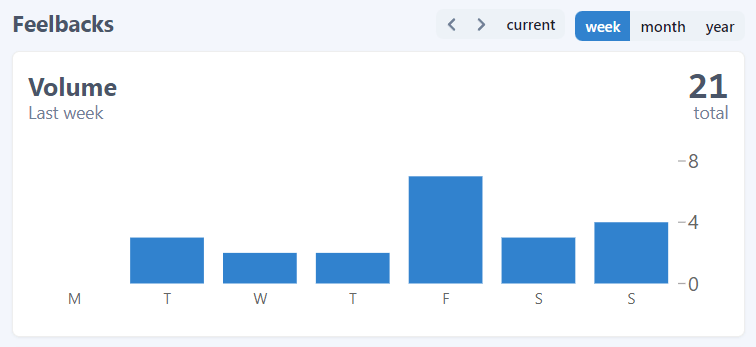
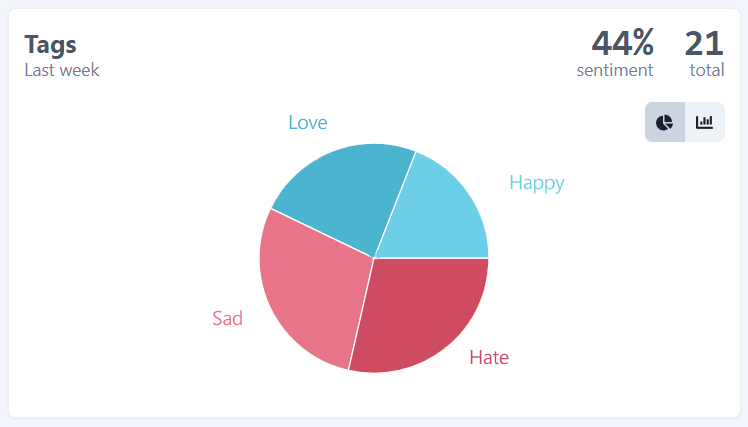
In this guide, we used the TaggedMessage to collect user feedbacks. And, because we configured sentiment values, Feelback creates sentiment aggregations too. For each page you can see the overall evaluation and the per Tag split.
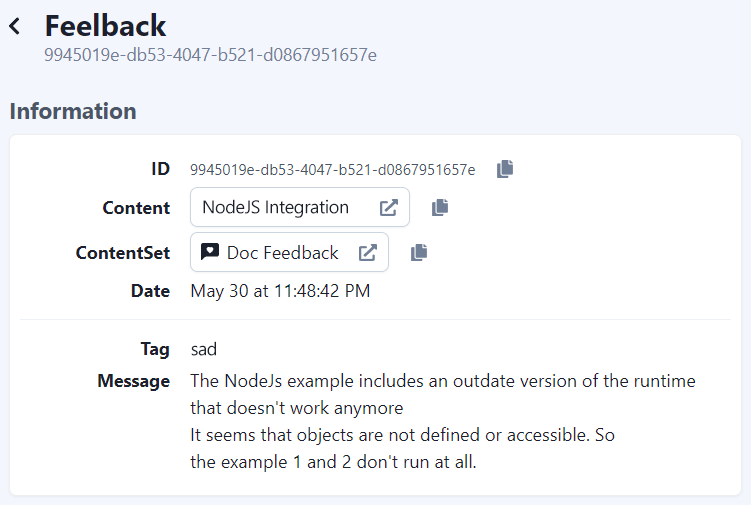
In addition to the aggregated view, you can go deep and analyze each single feedback. You can search, filter and check each feedback and see the details.
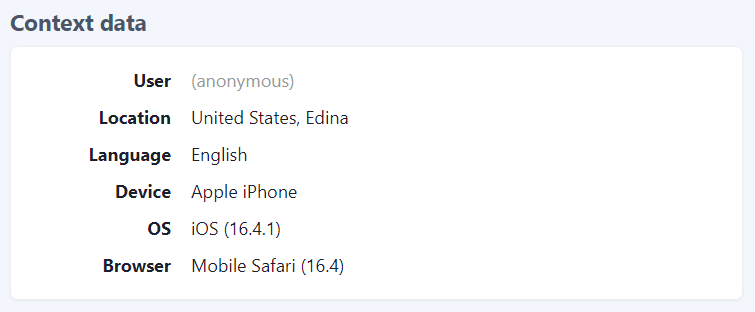
Each feedback comes with context data to further understand the relevance and specifics.
Additional resources
- Read the Feelback types list to know all signals you can receive from your users, from simple reactions or ratings to more complex error reporting or suggestion messages
- Checkout the integration guides to see all libraries, frameworks and website builder you can use with Feelback to collect user feedback